Introduction
In the intricate world of software development, documentation serves as the backbone of communication, traceability, and accountability. As software projects grow in complexity, the need for robust document review processes becomes increasingly vital. “Software Document Review” is not merely a procedural step but a strategic activity aimed at ensuring the accuracy, consistency, and quality of software documentation. This comprehensive article explores the significance, methodologies, tools, challenges, and best practices surrounding software document review within the software development lifecycle (SDLC).
Understanding Software Document Review
Software document review is the systematic examination of technical and non-technical documentation produced during the software development lifecycle. These documents may include requirements specifications, design documents, user manuals, test plans, source code comments, API documentation, release notes, and more.
The primary goals of document review include:
- Verifying accuracy and completeness
- Ensuring consistency with project standards and guidelines
- Identifying ambiguities or contradictions
- Confirming compliance with regulatory and industry standards
- Enhancing the overall quality of software deliverables
Types of Software Documentation Subject to Review
- Requirements Documentation
- Functional and non-functional requirements
- User stories and acceptance criteria
- Design Documentation
- Architecture diagrams
- Module specifications
- Database schema documentation
- Technical Documentation
- Source code comments
- API references
- Configuration guides
- Testing Documentation
- Test plans and cases
- Test reports and logs
- Defect tracking reports
- End-User Documentation
- User manuals
- Installation guides
- FAQs and troubleshooting guides
Importance of Software Document Review
Effective document review contributes to:
- Improved Communication: Clear, concise documentation bridges the gap between stakeholders.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifies errors or inconsistencies early in the development process.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures that documents meet legal and industry-specific requirements.
- Project Efficiency: Reduces rework and misunderstandings, streamlining project timelines.
- Customer Satisfaction: High-quality user documentation enhances user experience and reduces support needs.
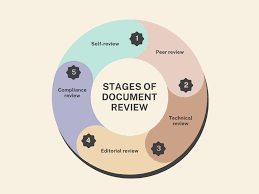
Methods of Document Review
- Peer Review
- Conducted by team members with similar technical backgrounds
- Focuses on accuracy and completeness
- Walkthroughs
- Author presents the document to a group for feedback
- Collaborative and educational approach
- Inspections
- Formal and structured process
- Roles include moderator, reader, recorder, and reviewers
- Uses checklists and predefined criteria
- Ad Hoc Reviews
- Informal, spontaneous reviews
- Useful for quick feedback but lacks consistency
Tools Supporting Software Document Review
- Microsoft Word/Google Docs: Track changes and comment features
- Atlassian Confluence: Collaborative documentation with version control
- GitHub/GitLab: Review markdown documents alongside code
- Document360: Knowledge base software with review workflows
- SharePoint: Enterprise document management and review
Review Criteria and Checklists
Checklists ensure that all critical aspects are evaluated. Typical criteria include:
- Correctness and accuracy
- Completeness of information
- Clarity and readability
- Consistency of terminology
- Compliance with style guides
- Alignment with project objectives
Roles and Responsibilities in Document Review
- Author: Prepares the document and incorporates feedback
- Reviewer: Evaluates content based on criteria
- Moderator: Facilitates formal review sessions
- Recorder: Documents feedback and action items
- Stakeholders: Provide domain-specific insights
Challenges in Software Document Review
- Time Constraints: Limited availability for thorough reviews
- Subjectivity: Differing opinions on documentation quality
- Lack of Standardization: Inconsistent review practices across teams
- Tool Limitations: Inadequate support for versioning and tracking
- Resistance to Feedback: Authors may be defensive about critiques
Best Practices for Effective Document Review
- Establish Clear Objectives: Define what the review aims to achieve
- Use Standardized Templates: Ensure uniformity in documentation
- Create Review Schedules: Allocate dedicated time for reviews
- Encourage Constructive Feedback: Promote a positive review culture
- Document Review Findings: Maintain records of issues and resolutions
- Integrate with SDLC: Align document review with development phases
Case Study: Improving Quality Through Document Review
A mid-sized software firm faced quality issues due to inconsistent documentation. By implementing a structured document review process:
- Review checklists were standardized
- Reviewers were trained on best practices
- A document management tool was introduced
The outcome:
- 30% reduction in documentation errors
- Faster onboarding of new team members
- Improved customer satisfaction with user guides
Software Document Review in Agile and DevOps
In Agile and DevOps environments, documentation must be dynamic and responsive. Strategies include:
- Living Documents: Continuously updated during sprints
- Review as Part of Definition of Done: Ensure documents are reviewed before completing a task
- Integrated Tools: Use tools like Jira, Confluence, and Git for seamless documentation
Compliance and Audit Considerations
Industries such as healthcare, finance, and aviation have strict documentation requirements. Effective reviews help:
- Ensure traceability and version control
- Meet ISO, HIPAA, or GDPR standards
- Prepare for external audits
Future Trends in Software Document Review
- AI-Powered Reviews: Tools that suggest improvements using natural language processing
- Automated Style Checkers: Grammarly-like tools tailored for technical writing
- Collaborative Cloud Platforms: Real-time co-authoring and review
- Blockchain for Document Integrity: Ensures immutability and authenticity
Conclusion
Software document review is a foundational activity that supports the success of software projects. It fosters collaboration, ensures clarity, and upholds quality across all phases of the development lifecycle. By adopting structured methodologies, leveraging appropriate tools, and cultivating a culture of constructive feedback, organizations can significantly enhance the effectiveness of their documentation efforts. As technology evolves, so too will the practices of document review, integrating automation and intelligence to meet the demands of modern software development.
Whether you’re a developer, tester, technical writer, or project manager, understanding and engaging in effective software document review is essential for delivering reliable and user-friendly software solutions.